New Technology for Wine Production
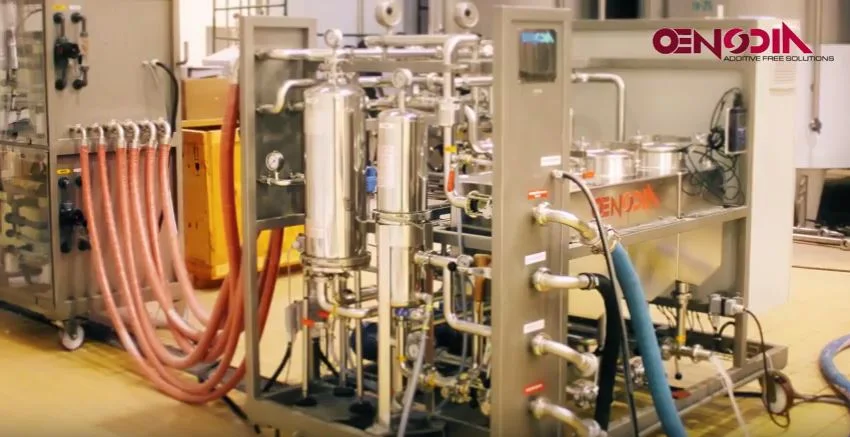
Electrodialysis
The Oenodia STARS system is an alternative treatment technology to remove tartrates without cold stabilization. This system can dramatically reduce the energy use associated with tartrate removal.
continuous Flash Cold Stabilization
TMCI Padovan Kristalstop Continuous Cold Stabilization system
The TMCI Padovan Kristalstop system continually cold stabilizes and utilizes a wine heat exchanger so that wine finishing cold stabilization can pre cool wine entering the system.
PIGGING/ICE PIGGING
Pigging involves using sponge balls know as Pipeline Inspection Gauges (PIGs), which can reduce water used in pushing wine and sanitizing lines. They can also reduce wine dilution and labor costs. Sonoma Wine Co. was able to retrofit several of their piping valves, which enabled them to use PIGs. This resulted in 10 -15% water savings in Sonoma Wine Co.’s cellar. E&J Gallo has also installed a double-PIG system at one of their wineries which uses a PIG at the beginning and end of a wine transfer.
Pigging can result in multiple benefits, but it will increase the use of nitrogen gas which will now be used for pushing where previously water had been used. Calculating the cost implications of increased nitrogen gas will determine whether this is a cost effective measure. Some valves and pipe work may need to be changed to accommodate a PIG system. Fully automotive PIGGing systems can cost thousands of dollars, however Sonoma Wine Co. was able to implement a more basic system for approximately $1,000.
Ice Pigging
Here are some applications where ice pigging can be used.
Must Transfer Lines - Ice Pigging has been successfully used by several wineries to separate juice batches in the must line. One winery, using a 3 to 5 foot ice PIG was able to significantly reduce its water use because with a solid ice separator they could push one juice batch with juice from the subsequent batch. The ice PIG forms a barrier to any mixing and a visual indicator to operators at the beginning and end of each juice transfer.
Wine Pushing - Ice Pigging can be very versatile adapting to changes in pipe diameter, 90 degree pipe turns, butterfly valves and most other pipe configurations. Using an ice pig to push wine minimizes any product loss or mixing.
Cleaning Transfer Lines - Ice causes abrasive action on the inside of wine transfer lines which can very effectively remove any debris on the outside of the line. Ice PIGs can be made with a caustic slurry to combine chemical cleaning with mechanical cleaning.
Caustic Capture and Reuse
Many of the common cleaning chemicals in the cellar can be captured and reused if they remain uncontaminated with dirt and debris. For tank cleaning, Caustic and Citric can be reused as long as they are periodically checked and adjusted to ensure they have the proper pH to be effective cleaners. Although less commonly discussed, it should also be possible to reuse Peracetic Acid (PAA). Research suggests that depending on the water chemistry and the concentration used, PAA has a half life between 8 to 30 hours, during which time it should be fine to reuse.
Capturing and reusing cleaning chemicals requires that a container or tank be available to store the cleaning solution.
Clean in Place (CIP) systems result in more efficient water use during sanitation, and in many cases allow the capture and reuse of portions of the fluids used in sanitation if they are uncontaminated in the cleaning process. This has the triple benefit of reducing water use, reducing chemical purchases and reducing the toxicity of water entering the wastewater treatment system.
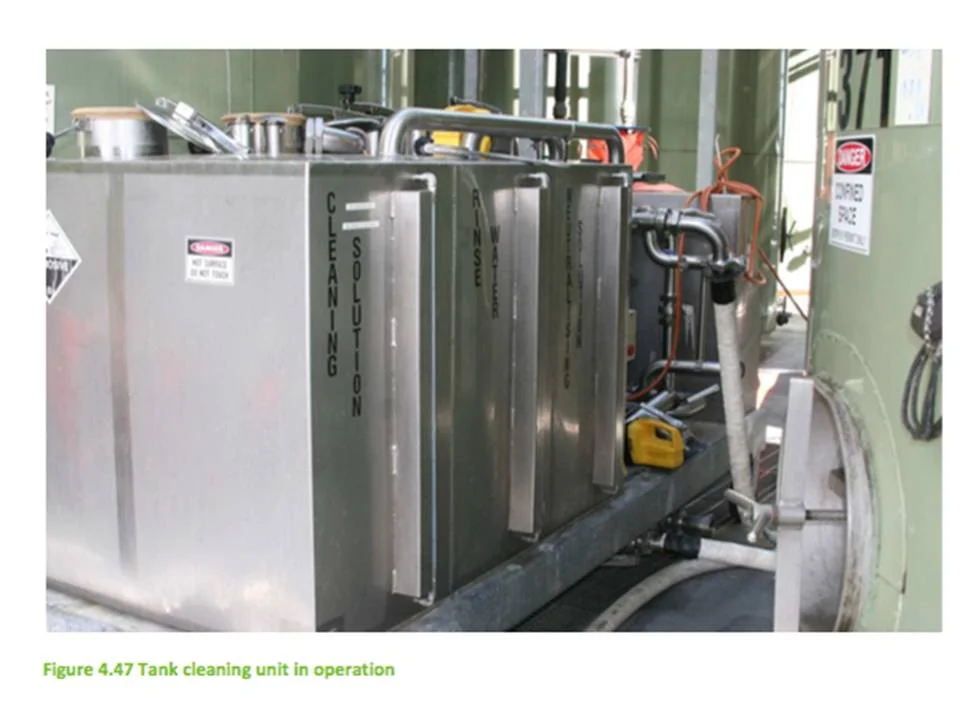
Examples of dedicated caustic piping for caustic reuse, caustic storage tanks for using caustic multiple times and a mobile tank washing unit capable or reusing caustic, citiric and rinse water from tank cleanings. Source: Winery Wastewater Management & Recycling Operational Guidelines - Australia’s Grape and Wine Research Development Corporation
Mobile Tank Washing Unit
A mobile tank washing unit is a CIP system capable of capturing and reusing water and cleaning solutions from a tank wash, line sanitation or equipment sanitation. This system is currently in use at the Oxford Landing Winery in Australia.
A mobile tank washing unit has the potential to achieve water savings of 70 to 85%, reduce chemical use by 90% and decrease staff time in tank cleanings. This provides water and cost saving benefits and would also provide significant benefits to wastewater treatment by minimizing chemical additions.
There are other methods of capturing and reusing water or cleaning solutions but they either require running hoses to a dedicated sump or sending water/cleaning solution to another tank about to be cleaned.
Inline Blending
Inline blending is a process that blends wine through a static mixer either as it is being transferred to a new destination or returning to its original destination. Inline blending has the potential to reduce tank washing and save staff time in the cellar.
To ensure batch consistency in large wine batches, many tanks may be used to ensure the wine is correctly blended. One vendor TechniBlend has an inline blending system that is capable of taking 3 different input steams and adjusting the percentage of each stream by weight with .5% accuracy. This system eliminates the need to use multiple tanks for blending as wine is mixed inline and returned to its original tank or sent to a different location.
A cheaper solution would be to use a static inline blending pipe, a “Y” valve, and hoses connected to multiple tanks. However, an automated system would have the advantage of providing very precise control.
Hydrofoils
Hydrofoils can be used to mix wine during the cold stabilization process. PG&E has calculated that hydrofoils can decrease the time it takes to cold stabilize wine by 60%. Reducing the time it takes to cold stabilize reduces facility energy use because cold stabilization is extremely energy intensive.
Blue Morph UV Light Sanitation
BlueMorph is a company that produces a UV sanitation system that uses only light to sanitize and can be used for both stainless steel tanks and wood barrels. This reduces the water, chemical and labor associated with sterilization. The current systems work on tanks of varying sizes and achieves a greater log reduction in removing microorganisms than conventional chemical sanitation methods. The system has low energy use and typically sanitizes a tank in under 30 minutes. http://www.bluemorphuv.com
MicroFog Sanitation
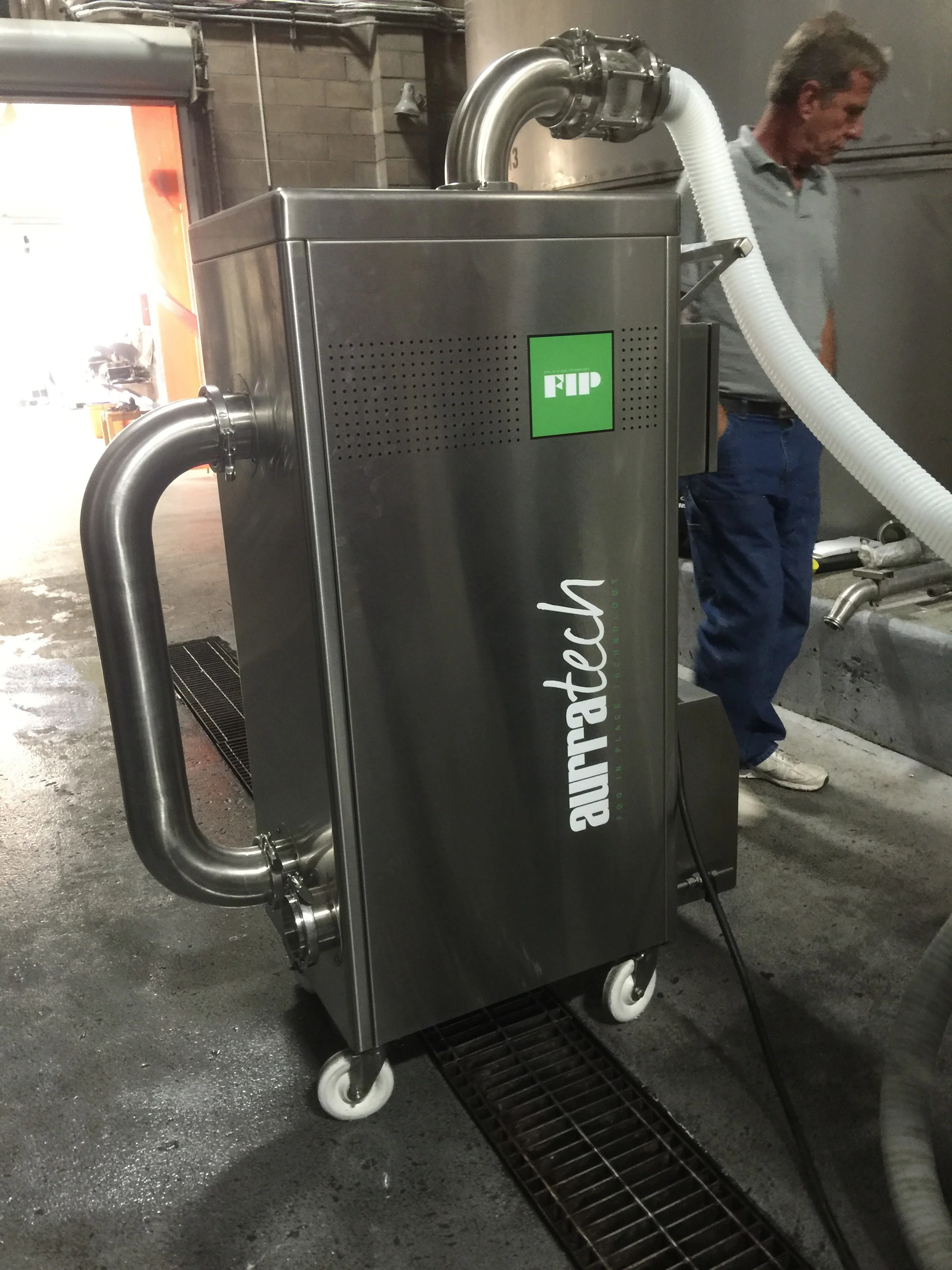
Aurratech uses a type of technology they call Fog in Place (FIP) that uses a fog with a sanitizer (many wineries use PAA) to clean the inside of a tank, a transfer line or any other equipment. Because it uses a fog instead of water, it can use both a fraction of the water normally required and a fraction of the chemical sanitizer needed as well. This technology was originally used in the orange juice industry.
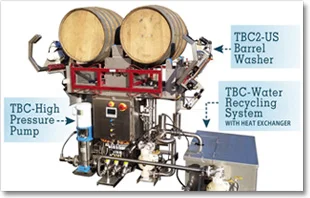
High Efficiency Barrel Washers
Tom Beard has developed barrel washing machines that can capture and reuse the clean rinse water from one barrel wash for cleaning the next barrel. This can reduce water use by 50% and reuse hot water leading to significant energy savings as well. In 2015 a large scale implementation of the project by Jackson Family Wines, won Environmental Leader's Top Project of the Year Award.
Source: Tom Beard Barrel Washers